DHCP Commands
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows hosts to join a network without having a preconfigured IP address. The setup requires a DHCP server to be present on the network. In large networks, DHCP servers provide IP configuration information for several subnets using DHCP relay agents running on each subnet.
DHCP Relay
RCP100 implements the relay agent functionality for each router interface. The functionality can be enabled on a per interface basis.
For redundancy and load balancing purposes, the relay agent can talk to multiple server groups. A group consists of not more than four DHCP servers. The relay sends the requests to all servers in the group. The servers in a group can implement any failover scheme available, such as the one described in RFC 2131.
If multiple groups are defined, the relay agent will load-balance randomly between groups. If the client fails to acquire an IP address, the request will be sent to all groups after a wait time specified by service-delay command.DHCP Server
RCP100 also implements DHCP server functionality.
Table Of Contents
clear ip dhcpdefault-router
domain-name
dns-server
host
ip dhcp relay
ip dhcp relay enable
ip dhcp server
lease
max-hops
network
ntp-server
option
range
server-group
service-delay
service dhcp
show ip dhcp
Example: DHCP relay
Example: DHCP server
clear ip dhcp
Clear DHCP statistics and leases.
clear ip dhcp statistics
Clear DHCP statistics
.clear ip dhcp lease [<ip address>]
Clear DHCP leases. If no IP address is specified, all leases are removed
.Example:
rcp#clear ip dhcp statistics rcp#clear ip dhcp lease 10.0.0.78
default-router
Set the default router advertized by DHCP server (DHCP option 3) for a specific network.
default-router <ip address>
no default-router
The no form removes the default router configuration.
Example:
rcp(dhcp server)#network 10.0.0.0/24 rcp(dhcp 10.0.0.0/24)#default-router 10.0.0.1
domain-name
Set the domain name advertized by DHCP server (DHCP option 15).
domain-name <domain>
no domain-name
The no form removes the domain name configuration.
Example:
rcp(dhcp server)#domain-name mycompany.com
dns-server
Set Domain Name Servers (DNS) advertized by DHCP server (DHCP option 6).
dns-server <ip address> [<ip address>]
Up to two DNS servers can be specified
no dns-server
The no form removes the DNS server configuration.
Example:
rcp(dhcp server)#dns-server 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4
host
Configure a static lease.
host <ip address> <mac address>
no host <ip address>
The no form removes the static lease.
Example:
rcp(dhcp server)#host 10.25.20.50 00:16:af:b5:39:a2
ip dhcp relay
Enter DHCP relay configuration mode.
ip dhcp relay
Use exit to return to global configuration mode.
no ip dhcp relay
The no form clears all the configuration entered in DHCP relay mode.
Example:
rcp(config)#ip dhcp relay rcp(dhcp relay)# ? exit Exit the current mode max-hops Maximum number of hops no Negate a command or set its defaults option Add DHCP Relay Agent Information (option 82) server DHCP primary server service-delay Delay before sending the request to all servers show Show running system information rcp(dhcp relay)# rcp(dhcp relay)#exit rcp(config)#
ip dhcp relay enable
The command is executed in interface configuration mode. It enables DHCP relay agent functionality for the interface.
ip dhcp relay enable
no ip dhcp relay enable
Example:
rcp(config)#interface ethernet eth0 rcp(config-if eth0)#ip dhcp relay enable rcp(config-if eth0)#
ip dhcp server
Enter DHCP server configuration mode.
ip dhcp server
Use exit to return to global configuration mode.
no ip dhcp server
The no form clears all the configuration entered in DHCP server mode.
Example:
rcp(config)#ip dhcp server rcp(dhcp server)# dns-server DNS server domain-name Domanin name exit Exit the current mode network Network no Negate a command or set its defaults ntp-server Network Time Protocol server show Show running system information rcp(dhcp server)#exit rcp(config)#
lease
Enter the lease for DHCP clients.
lease <days> <hours> <minutes>
no lease
The no form restores the default lease of one day.
Example:
The example sets a lease of four hours.rcp(dhcp server)#network 10.0.0.0/24 rcp(dhcp 10.0.0.0/24)#lease 0 4 0
max-hops
If the hop count field in DHCP packet is greater than max-hops, the packet is discarded.
max-hops <count>
no max-hops
The no form of the command restores the default of 4 hops.
network
Set a network for DHCP server and enter network mode.
network <CIDR address>
The network address is specified in CIDR format.
no network <CIDR address>
The no form removes the network configuration.
Example:
rcp(dhcp server)#network 10.0.0.0/24 rcp(dhcp 10.0.0.0/24)# default-router Default router exit Exit the current mode lease Lease time no Negate a command or set its defaults range Address range show Show running system information rcp(dhcp 10.0.0.0/24)#exit rcp(dhcp server)#
ntp-server
Set Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers advertized by DHCP server (DHCP option 42).
ntp-server <ip address> [<ip address>]
Up to two NTP servers can be specified.
no ntp-server
The no form removes the NTP server configuration.
Example:
rcp(dhcp server)#ntp-server 10.0.0.10 10.0.0.11
option
Insert a DHCP Relay Agent Information element (option 82) in the packet going to DHCP server. The element contains a Agent Circuit ID Sub-option (sub-option 1) in hostname.interface format. (e.g. rcp.eth0). If an option 82 is already present in the incoming packet, the packet is forwarded to the server as is.
option
no option
range
Set a range of IP addresses for DHCP clients on a specific network.
range <ip address> <ip address>
no range
The no form removes the client range configuration.
Example:
rcp(dhcp server)#network 10.0.0.0/24 rcp(dhcp 10.0.0.0/24)#range 10.0.0.50 10.0.0.200
server-group
Define a server group.
[no] server-group <address> [<address>] [<address>] [<address>]
The no form of the command removes the server group.
Example:
rcp(config)#ip dhcp relay rcp(dhcp relay)#server-group 10.1.20.70 10.1.20.71 rcp(dhcp relay)#server-group 10.1.20.72 10.1.20.73 rcp(dhcp relay)#show configuration dhcp ip dhcp relay server-group 10.1.20.70 10.1.20.71 server-group 10.1.20.72 10.1.20.73 ! rcp(dhcp relay)#
Two server groups are defined. Each group has two servers. Load balancing is done between the two groups with a default service-delay of 10 seconds.
service-delay
Delay before sending the requests to all server groups.
service-delay <seconds>
no service-delay
The no form of the command restores the default of 10 seconds.
When load-balancing between multiple server groups, if the client fails to acquire an IP address, the request is forwarded to all server groups. service-delay configures the time to wait before forwarding the request to everybody.
service dhcp
Enable DHCP server.
service dhcp
no service dhcp
The no form of the command disables the server.
Example:
rcp(config)#service dhcp
show ip dhcp
Show DHCP packet counts and statistics.
show ip dhcp
show ip dhcp interfaces
show ip dhcp leases
show ip dhcp servers
Example:
rcp(dhcp relay)#show ip dhcp interfaces Interface eth0 Total packets: RX 16004, TX 16001 Packets from/to clients: DHCPDISCOVER 8003 DHCPOFFER 8001 DHCPREQUEST 8001 DHCPACK 8000 DHCPDECLINE 0 DHCPNACK 0 DHCPRELEASE 0 DHCPINFORM 0 Interface eth1 Total packets: RX 8103, TX 0 Interface eth2 Total packets: RX 7898, TX 0 rcp(dhcp relay)#show ip dhcp servers Interface eth0 Total packets: RX 16004, TX 16001 Interface eth1 Total packets: RX 8103, TX 0 Packets from servers: DHCPOFFER 4052 DHCPACK 4051 DHCPNACK 0 Interface eth2 Total packets: RX 7898, TX 0 Packets from servers: DHCPOFFER 3949 DHCPACK 3949 DHCPNACK 0 rcp(dhcp relay)#
Example: DHCP Relay
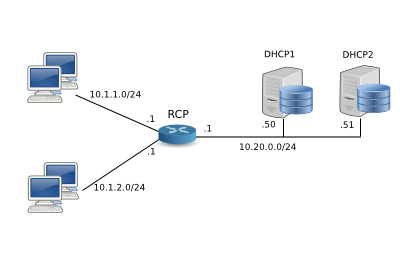
DHCP1 and DHCP2 are ISC DHCP servers running on regular Linux/*BSD computers. The IP ranges served are non-overlapping. Each server can service all the clients in the network, in case the other one dies. RCP router forwards requests randomly to both servers. If the client doesn't manage to get an IP address in 10 seconds, his requests are sent to both servers.
ISC DHCP server configuration, usually located in /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf, could look something like:
# DHCP1 server
subnet 10.20.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
}
subnet 10.1.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 10.1.1.50 10.1.1.149;
}
subnet 10.1.2.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 10.1.2.50 10.1.2.149;
}
and
# DHCP2 server
subnet 10.20.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
}
subnet 10.1.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 10.1.1.150 10.1.1.250;
}
subnet 10.1.2.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 10.1.2.150 10.1.2.250;
}
RCP configuration:
hostname rcp ! administrator rcp encrypted password QFSNKPHJ$kNBAqXTxlxZhwKWIpt1e61 ! ip dhcp relay server-group 10.20.0.50 server-group 10.20.0.51 ! interface loopback lo ip address 127.0.0.1/8 ip mtu 16436 no shutdown ! interface ethernet eth0 ip address 10.1.1.1/24 ip mtu 1500 ip dhcp relay enable no shutdown ! interface ethernet eth1 ip address 10.1.2.1/24 ip mtu 1500 ip dhcp relay enable no shutdown ! interface ethernet eth2 ip address 10.20.0.1/24 ip mtu 1500 no shutdown !
Example: DHCP Server
This is a sample configuration for a DHCP server handling two network segments.
rcp#show configuration dhcp
service dhcp
ip dhcp server
domain-name mycompany.com
dns-server 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4
ntp-server 10.0.0.22 10.1.0.22
network 10.0.0.0/24
range 10.0.0.205 10.0.0.250
default-router 10.0.0.1
lease 0 4 0
!
network 10.1.0.0/24
range 10.1.0.50 10.1.0.100
default-router 10.1.0.1
lease 0 4 0
!
!
rcp#
The leases can be displayed using show ip dhcp leases command:
rcp#show ip dhcp leases MAC Address IP Address Lease (hh:mm:ss) 00:58:22:33:00:09 10.0.0.214 03:59:54 00:58:22:33:00:08 10.0.0.213 03:59:54 00:58:22:33:00:03 10.0.0.208 03:59:54 00:58:22:33:00:02 10.0.0.207 03:59:54 00:58:22:33:00:01 10.0.0.206 03:59:54 00:58:22:33:00:00 10.0.0.205 03:59:54 00:58:22:33:00:07 10.0.0.212 03:59:54 00:58:22:33:00:06 10.0.0.211 03:59:54 00:58:22:33:00:05 10.0.0.210 03:59:54 00:58:22:33:00:04 10.0.0.209 03:59:54 rcp#
Specific leases can be removed using clear ip dhcp lease command:
rcp#clear ip dhcp lease 10.0.0.210
