DNS Commands
Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical distributed naming system used to translate resource names to IP addresses. DNS makes it possible to assign domain names to groups of Internet resources and users in a meaningful way, independent of each entity's physical location.
RCP100 implements the standard DNS facilities necessary to connect to Internet. It also features a DNS proxy. The proxy forwards the requests to a configured DNS server and maintains a cache entry for each resolved DNS query. The cached entries are used to speed up future queries. This offloads remote DNS servers and reduces response time for DNS lookups.


Each cache entry has associated a time-to-live (TTL) timer. RCP100 will remove the entry once the timer expires. The maximum value for TTL is hard-coded to 15 minutes. RCP100 also allows to manually add and remove entries from the cache.
Another typical usage for DNS proxy cache is to implement what is generally called a "split-horizon DNS". In a split DNS configuration, resources such as web servers are available under different IP addresses for the people on internal and external networks. This is mainly the case with servers placed in DMZ. The DNS global entry for such a server will report an external address unreachable from the internal network. The problem is solved by adding a static host entry in DNS proxy cache. Static proxy entries can also be used to assign name to hosts located on internal networks.
Table Of Contents
clear ip hostip dns server
hostname
ip domain-name
ip host
ip name-server
show ip dns statistics
show ip host
Example
clear ip host
Clear all DNS cached entries.
clear ip host
ip dns server
Enable DNS proxy cache.
ip dns server [rate-limit <limit>]
no ip dns server
where:
rate-limit - optional rate limit of packets forwarded to servers
no form of the command disables the proxy.
hostname
Set router hostname.
hostname <name>
no hostname
no form of the command restores the default rcp.
Example:
rcp(config)#hostname lab1 lab1(config)#no hostname rcp(config)#
Note: the hostname is reflected in the command prompt.
ip domain-name
Configure the default domain name RCP uses to resolve unqualified host names (names without a dotted-decimal domain suffix).
ip domain-name <name>
no ip domain-name
no form of the command removes the configuration.
Example:
rcp(config)#ip domain-name mycompany.com rcp(config)#
ip host
Map a name to an IP address. If DNS proxy is enabled, an entry is added to proxy cache.
ip host <name> <IP address>
no ip host <name>
no form of the command removes the mapping.
Example:
rcp(config)#ip host www.mycompany.com 10.200.0.70 rcp(config)#
ip name-server
Configure an external DNS server to forward the queries. Two such servers can be configured.
ip name-server <IP address>
no ip name-server <IP address>
no form of the command removes the server.
Example:
rcp(config)#ip name-server 8.8.8.8 rcp(config)#
show ip dns statistics
Show DNS proxy cache statistics.
show ip dns statistics
Example:
rcp#show ip dns statistics DNS queries: 4759 packets DNS answers: 4734 packets DNS cached answers: 1266 packets RR types: A: 509 packets CNAME: 1858 packets PTR: 3 packets MX: 0 packets AAAA (IPv6): 36 packets Request queue 0 rcp#
show ip host
Show the proxy cache.
show ip host
Example:
rcp#show ip host Name Address TTL mirror.us.leaseweb.net 108.59.10.97 357 sourceforge.net 216.34.181.60 342 fonts.googleapis.com 72.14.204.95 134 chi-10g-1-mirror.fastsoft.net 208.78.26.135 150 mirror.us.as6453.net 209.58.29.74 106 a.fsdn.com 184.50.243.172 12 html5center.sourceforge.net 216.34.181.150 899 geek.net 216.34.181.202 899 www.google.com 173.194.73.103 213 themes.googleusercontent.com 74.125.226.203 217 sourceforge.jp 202.221.179.21 899 twitter.com 199.59.150.7 23 rcp#
Example
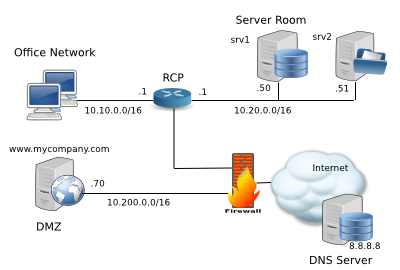
RCP100 is connecting the office network (interface eth0), the server network (eth1) and the firewall (eth2).
interface ethernet eth0 ip address 10.10.0.1/16 ip mtu 1500 no shutdown ! interface ethernet eth1 ip address 10.20.0.1/16 ip mtu 1500 no shutdown ! interface ethernet eth2 ip address 10.30.0.10/16 ip mtu 1500 no shutdown !
The master DNS server is provided by the Internet service provider (8.8.8.8 in this example), and the company is known by the outside world as mycompany.com.
ip name-server 8.8.8.8 ip domain-name mycompany.com
Enabling DNS proxy cache allows the office users to access the company web server at 10.200.0.70 as www.mycompany.com, and the servers in the server room as srv1.mycompany.com and srv2.mycompany.com. Short names such as www, srv1, srv2 entered in the web browser will also be translated to the correct IP address.
ip dns server ip host www.mycompany.com 10.200.0.70 ip host srv1.mycompany.com 10.20.0.50 ip host srv2.mycompany.com 10.20.0.51
The relevant DNS configuration is as follows:
rcp(config)#show configuration dns hostname rcp ip name-server 8.8.8.8 ip domain-name mycompany.com ip host www.mycompany.com 10.200.0.70 ip host srv1.mycompany.com 10.20.0.50 ip host srv2.mycompany.com 10.20.0.51 ip dns server ! rcp(config)#

